Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Early disease detection is a prerequisite for enacting effective interventions for disease control. Strains of the bacterial plant pathogen
Xylella fastidiosa
have recurrently spread to new crops in new countries causing devastating outbreaks. So far, investigation of outbreak strains and highly resolved phylogenetic reconstruction have required whole-genome sequencing of pure bacterial cultures, which are challenging to obtain due to the fastidious nature of
X. fastidiosa
. Here, we show that culture-independent metagenomic sequencing, using the Oxford Nanopore Technologies MinION long-read sequencer, can sensitively and specifically detect the causative agent of Pierce’s disease of grapevine,
X. fastidiosa
subspecies
fastidiosa
. Using a DNA sample from a grapevine in Virginia, USA, it was possible to obtain a metagenome-assembled genome (MAG) of sufficient quality for phylogenetic reconstruction with SNP resolution. The analysis placed the MAG in a clade with isolates from Georgia, USA, suggesting introduction of
X. fastidiosa
subspecies
fastidiosa
to Virginia from the south-eastern USA. This proof of concept study, thus, revealed that metagenomic sequencing can replace culture-dependent genome sequencing for reconstructing transmission routes of bacterial plant pathogens.
Genus Pseudoxanthomonas represents a relatively newly characterized group of gamma-proteobacterium of environmental origin. Species of the genus have very similar morphology to strains belonging to Xanthomonas, Xylella and Stenotrophomonas. However, the genome resource of this g …
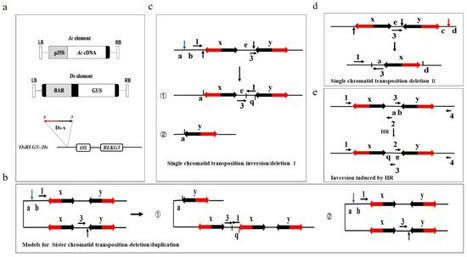
Rice bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) seriously affects rice yield production. The discovery and application of broad-spectrum resistance genes are of great advance for disease resistance breeding. Previously, we identified that multiple receptor-like kinase (RLK) family gene deletions induced by the Ac/Ds system resulted in a lesion mimic symptom. In this study, the mutant #29 showed that this lesion mimic symptom was isolated. Further analysis identified that four RLK genes (RLK19-22) were deleted in the #29 mutant. The #29 mutant exhibited broad-spectrum resistance to Xoo and subsequent analyses identified that pathogenesis-related genes PR1a, PBZ1, and cellular H2O2 levels were significantly induced in the mutant compared to wild-type plants. A genetic analysis revealed that reconstruction of RLK20, RLK21, or RLK22 rescued the lesion mimic symptom of the #29 mutant, indicating that these three RLKs are responsible for broad-spectrum resistance in rice. Further yeast two hybrid and bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays demonstrated that RLK20 interacts with RBOHB, which is a ROS producer in plants. Compared to wild-type plants, the #29 mutant was more, while #29/RLK20ox was less, susceptible to MV (methyl-viologen), an ROS inducer. Co-expression of RLK20 and RBOHB reduced RBOHB-promoted H2O2 accumulation in the cells. Taken together, our research indicated that the RLKs may inhibit RBOHB activity to negatively regulate rice resistance to Xoo. These results provide the theoretical basis and valuable information about the target genes necessary for the successful breeding of rice cultivars resistant to bacterial blight.
The growing concern regarding the potential risks of pesticides and their impact on non-target organism stimulates the development and application of alternative, environmentally-friendly products. It seems necessary to develop alternatives for conventional products and for those already widely used in organic agriculture, e.g. copper. Very importantly, such alternative products should not limit the productivity and profitability of agriculture. In this study, we examined the efficacy of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) leaf extract as such an alternative. We tested its impact on the virulence of Pseudomonas syringae towards the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana and the crop plant tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) as well as of Clavibacter michiganensis, Xanthomonas campestris and Phytophthora infestans towards tomato, at multiple levels. We could demonstrate that licorice leaf extract acts as direct fungicide and bactericide. Moreover, it acts against a metalaxyl-resistant P. infestans strain. In addition, the extract from licorice leaves influences the plant immune system, modulating the plant responses to the challenge with pathogen(s), this involves both salicylic acid and ethylene-based responses. Our results show that in addition to the well-known use of licorice root extract in medicine, the leaf extract can be an effective alternative in organic and integrated farming, contributing to copper reduction and resistance management.
Pathovars of Xanthomonas campestris (Xc) cause distinct diseases on different brassicaceous hosts. The genomic relationships among pathovars as well as the genetic determinants of host range and tissue specificity remain poorly understood despite decades of research. Here, leveraging advances in multiplexed long-read technology, we fully sequenced the genomes of a collection of Xc strains isolated from cruciferous crops and weeds in New York and California, as well as strains from global collections, to investigate pathovar relationships and candidate genes for host- and tissue-specificity. Pathogenicity assays and genomic comparisons across this collection and publicly available Xc genomes revealed a correlation between pathovar and genomic relatedness and provide support for Xc pv. barbareae, the validity of which had been questioned. Linking strain host range with type III effector repertoires identified AvrAC (also ‘XopAC’) as a candidate host-range determinant, preventing infection of Matthiola incana, and this was confirmed experimentally. Furthermore, the presence of a copy of the cellobiosidase gene cbsA with coding sequence for a signal peptide was found to correlate with the ability to infect vascular tissues, in agreement with a previous study of diverse Xanthomonas species; heterologous expression in strains lacking the gene gave mixed results however, indicating that factors in addition to cbsA influence tissue specificity of Xc pathovars.
Phytochromes, found in plants, fungi, and bacteria, exploit light as a source of information to control physiological processes via photoswitching between two states of different physiological activity, i.e. a red-absorbing Pr and a far-red-absorbing Pfr state. Depending on the relative stability in the dark
PreviousNext Resource Announcement OPENOpen Access licenseComplete Genome Sequence Data of Two Xanthomonas arboricola Strains Isolated from Blueberry Plants Displaying Bacterial Leaf Blight in PolandMonika Kałużna and Joël F. Pothier AffiliationsAuthors and Affiliations Monika Kałużna1 † Joël F.
Network science identifies key players in diverse biological systems including host-pathogen interactions. We demonstrated a scale-free network property for a comprehensive rice protein-protein interactome (RicePPInets) that exhibits nodes with increased centrality indices. While weighted k-s …
Xylella fastidiosa is the etiological agent of Plum Leaf Scald (Greco et al. 2021). The disease was first reported in Argentina (Fernandez-Valiela et al. 1954) and then Brazil and Paraguay (French et al. 1978). In the USA, Plum Leaf Scald has been reported in the Southeastern United States (W …
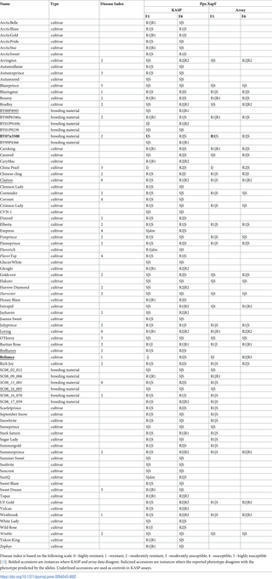
Bacterial spot, caused by Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni (Xap), is a serious peach disease with symptoms that traverse severe defoliation and black surface pitting, cracking or blemishes on peach fruit with global economic impacts. A management option for control and meeting consumer demand for chemical-free, environmentally friendly fruit production is the development of resistant or tolerant cultivars. We developed simple, accurate, and efficient DNA assays (Ppe.XapF) based on SNP genotyping with KASP technology to quickly test for bacterial spot resistance alleles in peach fruit that allows breeders to cull seedlings at the greenhouse stage. The objective of this research was to validate newly developed DNA tests that target the two major QTLs for fruit resistance in peach with diagnostic utility in predicting fruit response to bacterial spot infection. Our study confirms that with only two Ppe.XapF DNA tests, Ppe.XapF1-1 and Ppe.XapF6-2, individuals carrying susceptible alleles can be identified. Use of these efficient and accurate Ppe.XapF KASP tests resulted in 44% reduction in seedling planting rate in the Clemson University peach breeding program.
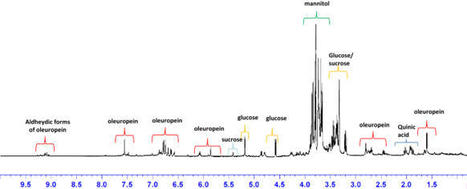
Xylella fastidiosa is a xylem-limited bacterium causing a range of economically important plant diseases in hundreds of crops. Over the last decade, a severe threat due to Olive Quick Decline Syndrome (OQDS), caused by Xylella fastidiosa subspecies pauca, affected the Salento olive groves (Apulia, South-East Italy). Very few phyto-therapeutics, including a Zn/Cu citric acid biocomplex foliar treatment, were evaluated to mitigate this disease. However, the traditional foliar applications result in the agro-actives reaching only partially their target. Therefore the development of novel endo-therapeutic systems was suggested. Metabolite fingerprinting is a powerful method for monitoring both, disease progression and treatment effects on the plant metabolism, allowing biomarkers detection. We performed, for the first time, short-term monitoring of metabolic pathways reprogramming for infected Ogliarola salentina and Cima di Melfi olive trees after precision intravascular biocomplex delivery using a novel injection system. Upon endo therapy, we observed specific variations in the leaf content of some metabolites. In particular, the 1H NMR-based metabolomics approach showed, after the injection, a significant decrease of both the disease biomarker quinic acid and mannitol with simultaneous increase of polyphenols and oleuropein related compounds in the leaf’s extracts. This combined metabolomics/endo-therapeutic methodology provided useful information in the comprehension of plant physiology for future applications in OQDS control.
Xylella fastidiosa is a plant pathogenic bacterium that has been introduced in the European Union (EU), causing significant yield losses in economically important Mediterranean crops. Almond leaf scorch (ALS) is currently one of the most relevant diseases observed in Spain, and no cure has been found to be effective for this disease. In previous reports, the peptide BP178 has shown a strong bactericidal activity in vitro against X. fastidiosa and to other plant pathogens, and to trigger defense responses in tomato plants. In the present work, BP178 was applied by endotherapy to almond plants cv. Avijor using preventive and curative strategies. The capacity of BP178 to reduce the population levels of X. fastidiosa and to decrease disease symptoms, and its persistence over time were demonstrated under greenhouse conditions. The most effective treatment consisted of a combination of preventive and curative applications and the peptide was detected in the stem up to 60 days post-treatment. Priming plants with BP178 induced defense responses mainly through the salicylic acid pathway, but also overexpressed some genes of the jasmonic acid and ethylene pathways. It is concluded that the bifunctional peptide is a promising candidate to be further developed to manage ALS caused by X. fastidiosa.
Understanding plant’s response mechanisms against pathogenesis is fundamental for the development of resistant crop varieties and more productive agriculture. In this regard, “omic” approaches are heralded as valuable technologies. In this work, combining isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ) technology with mass spectrometry, the proteomes from leaves of Brassica oleracea plants infected with Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc), and control plants at two different post-infection times were compared. Stronger proteomic changes were obtained at 12 days post-infection in comparison with 3 days. The responses observed involved different cell processes, from primary metabolism, such as photosynthesis or photorespiration, to other complex processes such as redox homeostasis, hormone signaling, or defense mechanisms. Most of the proteins decreased in the earlier response were involved in energetic metabolism, whereas later response was characterized by a recovery of primary metabolism. Furthermore, our results indicated that proteolysis machinery and reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis could be key processes during this plant–pathogen interaction. Current data provide new insights into molecular mechanisms that may be involved in defense responses of B. oleracea to Xcc.
|
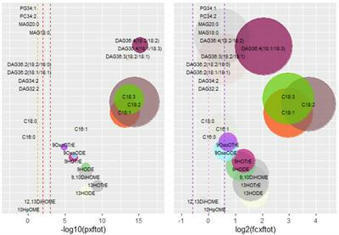
In 2013, Xylella fastidiosa (Xf) was detected for the first time in Apulia and, subsequently, recognized as the causal agent of the olive quick decline syndrome (OQDS). To contain the disease, the olive germplasm was evaluated for resistance to Xf, identifying cultivars with different susceptibility to the pathogen. Regarding this, the resistant cultivar Leccino has generally a lower bacterial titer compared with the susceptible cultivar Ogliarola salentina. Among biomolecules, lipids could have a pivotal role in the interaction of Xf with its host. In the grapevine Pierce’s disease, fatty acid molecules, the diffusible signaling factors (DSFs), act as regulators of Xf lifestyle and are crucial for its virulence. Other lipid compounds derived from fatty acid oxidation, namely, oxylipins, can affect, in vitro, biofilm formation in Xf subsp. pauca (Xfp) strain De Donno, that is, the strain causing OQDS. In this study, we combined high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-MS-based targeted lipidomics with supervised learning algorithms (random forest, support vector machine, and neural networks) to classify olive tree samples from Salento. The dataset included samples from either OQDS-positive or OQDS-negative olive trees belonging either to cultivar Ogliarola salentina or Leccino treated or not with the zinc-copper-citric acid biocomplex Dentamet®. We built classifiers using the relative differences in lipid species able to discriminate olive tree samples
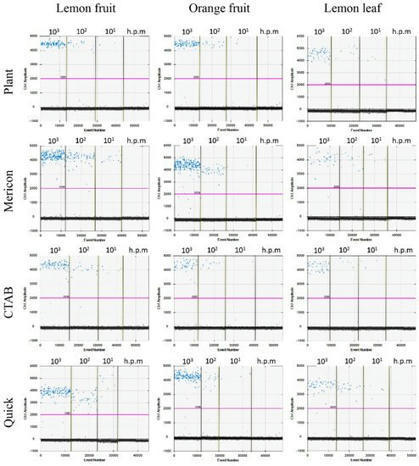
Xanthomonas citri pv. citri (Xcc) and X. citri pv. aurantifolii (Xca), causal agents of citrus bacterial canker, are both regulated by the European Union to prevent their introduction. Xcc is responsible for severe outbreaks of citrus production worldwide, therefore, a prompt and reliable detection is advisable for the early detection of this bacterium either in symptomatic or asymptomatic plant material. The current EPPO (European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization) diagnostic protocol, PM 7/44(1), includes several diagnostic tests even if new assays have been developed in the latter years for which validation data are needed. Recently, a test performance study was organized within the Valitest EU Project to validate Xcc diagnostic methods and provide evidence on the most reliable assays; however, the influence of DNA extraction methods (DEM) on the reliability of the detection has never been assessed. In this study we evaluate four different DEM, by following two different approaches: (i) a comparison by real-time PCR standard curves of bacterial DNA versus bacterial DNA added to plant DNA (lemon, leaves and fruit; orange fruit); and (ii) the evaluation of performance criteria of spiked samples (plant extract added with ten-fold diluted bacterial suspensions at known concentrations). Droplet digital PCR is developed and compared with real-time PCR, as the detection method.
PreviousNext Resource Announcement OPENOpen Access licenseComplete Genome Sequence Resource for Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa MAI5034, a Wheat Pathogen from UruguayFelipe Clavijo, Claudia Barrera, Aleksander Benčič, Valentina Croce, Jonathan M. Jacobs, Adriana J.
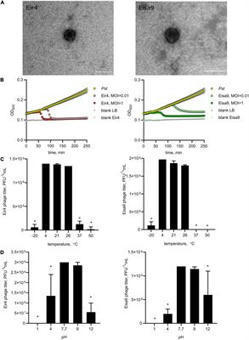
Pseudomonas syringae is a bacterial pathogen that causes yield losses in various economically important plant species. At the same time, P. syringae pv. tomato (Pst) is one of the best-studied bacterial phytopathogens and a popular model organism. In this study, we report on the isolation of two phages from the market-bought pepper fruit showing symptoms of bacterial speck. These Pseudomonas phages were named Eir4 and Eisa9 and characterized using traditional microbiological methods and whole-genome sequencing followed by various bioinformatics approaches. Both of the isolated phages were capable only of the lytic life cycle and were efficient against several pathovars from Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas genera. With the combination of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) virion morphology inspection and comparative genomics analyses, both of the phages were classified as members of the Autographiviridae family with different degrees of novelty within the known phage diversity. Eir4, but not Eisa9, phage application significantly decreased the propagation of Pst in the leaf tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana plants. The biological properties of Eir4 phage allow us to propose it as a potential biocontrol agent for use in the prevention of Pst-associated bacterioses and also as a model organism for the future research of mechanisms of phage–host interactions in different plant systems.
Microorganisms with biocontrol capabilities against plant pathogens are considered as one of the most promising approaches for healthy crop management. In this study, ethyl acetate extracts of 25 Bacillus strains were investigated for their antagonistic effect on Xanthomonas citri subs …
Given these profiles of target compounds, we highlight a new strategy for controlling intractable plant bacterial diseases by inducing plant resistance and targeting the bacterial cell membrane. © 2022 Society of Chemical Industry.
PreviousNext Resource Announcement OPENOpen Access licenseComplete Genome Sequence Resources of Six Strains of the Most Virulent Pathovars of Xanthomonas arboricola Using Long- and Short-Read Sequencing ApproachesSara Cuesta-Morrondo, Cristina Redondo, Ana Palacio-Bielsa, Jerson Garita-Cambronero,...
Bacterial leaf spot (BLS) of lettuce caused by Xanthomonas hortorum pv. vitians (Xhv) was first described over 100 years ago and remains a significant threat to lettuce cultivation today. This study investigated the genetic relatedness of the Xhv strains and the possible genetic sources of this race-specific pathogenicity. Whole genome sequences of eighteen Xhv strains representing the three races, along with eight related Xanthomonas strains, were included in the analysis. A maximum likelihood phylogeny based on concatenated whole genome SNPs confirmed previous results describing two major lineages of Xhv strains. Gene clusters encoding secretion systems, secondary metabolites, and bacteriocins were assessed to identify putative virulence factors that distinguish the Xhv races. Genome sequences were mined for effector genes, which have been shown to be involved in race specificity in other systems. Two effectors identified in this study, xopAQ and the novel variant xopAF2, were revealed as possible mediators of a gene-for-gene interaction between Xhv race 1 and 3 strains and wild lettuce Lactuca serriola ARM-09-161-10-1. Transposase sequence identified downstream of xopAF2 and prophage sequence found nearby within Xhv race 1 and 3 insertion sequences suggest that this gene may have been acquired through phage-mediated gene transfer. No other factors were identified from these analyses that distinguish the Xhv races.
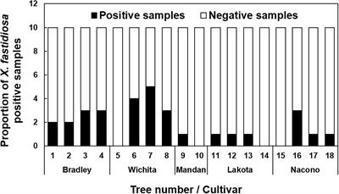
Pecan bacterial leaf scorch, caused by Xylella fastidiosa subsp. multiplex, is an economically significant disease of pecan with known detrimental effects on the yield of susceptible cultivars. In this study, endosperm was harvested from developing pecan seeds, and direct qPCR and sequencing were used to detect and confirm the presence of X. fastidiosa. DNA was isolated from mature seeds originating from seven trees, revealing a positivity rate up to 90%, and transmission of X. fastidiosa from infected seed to the germinated seedlings was found to be over 80%. Further epidemiological analyses were performed to determine where X. fastidiosa localizes in mature seed and seedlings. The highest concentrations of X. fastidiosa DNA were found in the hilum and outer integument of the seeds and the petioles, respectively. High-, medium-, and low-density seeds were harvested to determine the impact of the bacterium on seed density and seedling growth rate. The growth rate of seedlings originating from low-density seeds was significantly reduced compared to the medium- and high-density seeds. Despite the increased growth and germination rates, the high-density seed group had a greater proportion of samples that tested positive for the presence of X. fastidiosa by qPCR. The results demonstrate the ability of X. fastidiosa to colonize developing seeds and be efficiently transmitted from well-developed seeds to germinated seedlings. Continued research is needed to understand th
SWEETs play important roles in intercellular sugar transport. Induction of SWEET sugar transporters by Transcription Activator-Like effectors (TALe) of Xanthomonas ssp. is key for virulence in rice, cassava and cotton. We identified OsSWEET11b with roles in male fertility and potential bacterial bli …
Arzone, A., Vidano, C. & Alma, A. (1987) Auchenorrhyncha introduced to Europe from the Nearctic Region; taxonomic and phytopathological problems. In: Wilson, M.R. & Nault, L.R. (Eds.), Proceedings of 2nd International Workshop on Leafhoppers and Planthoppers of Economic Importance. C.A.B.
In Southern Italy, since 2013, there has been an ongoing Olive Quick Decline Syndrome (OQDS) outbreak, due to the bacterium Xylella fastidiosa, which has caused a dramatic impact from both socio-economic and environmental points of view. The main players involved in OQDS are represented by the insec …
|





 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...